Jan 18, 2022 · 2 min read
2 Stanford Researchers Are Using AI To See More in the Brain
From Parkinson’s to Alzheimer’s, neurodegenerative diseases are on the rise — yet few therapies exist to combat them. That’s why the  program at CZI’s
program at CZI’s  (NDCN) is bringing together scientists to explore new ideas and new approaches.
(NDCN) is bringing together scientists to explore new ideas and new approaches.
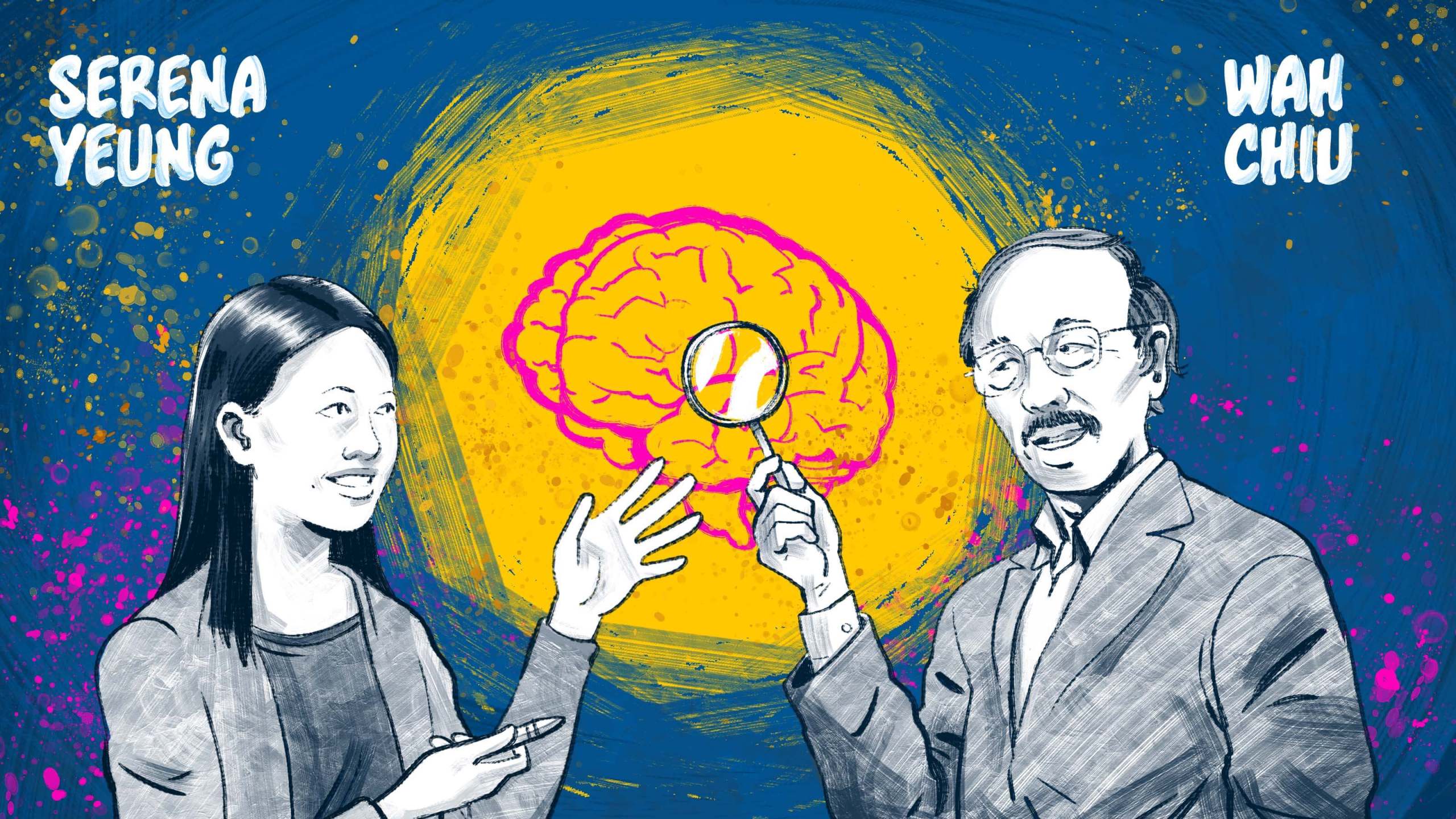
Stanford researchers Wah Chiu and Serena Yeung bring unconventional perspectives to bear on brain research. He has been pioneering the use of cryo-electron microscopy to see molecules at the atomic scale. She explores new approaches to artificial intelligence and machine learning for biomedicine and healthcare. Their joint technical expertise could reveal the inner workings of neurons in unprecedented detail, as part of a new project supported by the  .
.
Get to know how the  in order to accelerate the science of neurodegeneration — and ultimately, the path to treatments.
in order to accelerate the science of neurodegeneration — and ultimately, the path to treatments.

Imagine an alien visiting a city on Earth for the first time. How would it make sense of everything going on?

Neuroscience has a similar problem. Despite a lot of technological progress, people don’t really know all the details of what happens inside a neuron.

If we want to understand how the brain works and how to fix it, we need better ways to look inside it and its cells.
Microscopes can show us some pieces, including individual molecules. But putting the pieces together is complicated.

We think artificial intelligence (AI) can help. We are not neuroscientists. But we have a lot of friends who are!

We’re applying computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers and systems to derive meaningful information from digital images, captured from microscopes, to identify and classify molecules and their interactions.

This will allow us to compare healthy cells to unhealthy cells with mutations linked to Huntington’s disease. Our findings can also help us develop data and workflows that could open the opportunity for broader application of computer vision and deep learning algorithms to other neurodegenerative diseases.
 about how the NDCN empowers scientists to pursue bold ideas in order to accelerate the science of neurodegeneration — and ultimately, the path to treatments.
about how the NDCN empowers scientists to pursue bold ideas in order to accelerate the science of neurodegeneration — and ultimately, the path to treatments.